Choosing a domain is one of the very first and most important steps when it comes to building a website. Your domain name isn’t just your digital address; it helps with your brand’s visibility, memorability, and even credibility. Domains come in many forms and each was designed with different needs and purposes in mind. In this blog, we will dive deeper into the different types of domains that exist, explaining their unique attributes and how they impact your online presence.
What is a Domain Name?
Practically, first things first. The domain name is the address one types in a browser’s URL bar to get onto a website, such as “www.example.com.” In simple terms, it is the human-readable version of the IP address of your website to make it easier to find by people.

Top Level Domains (TLDs)
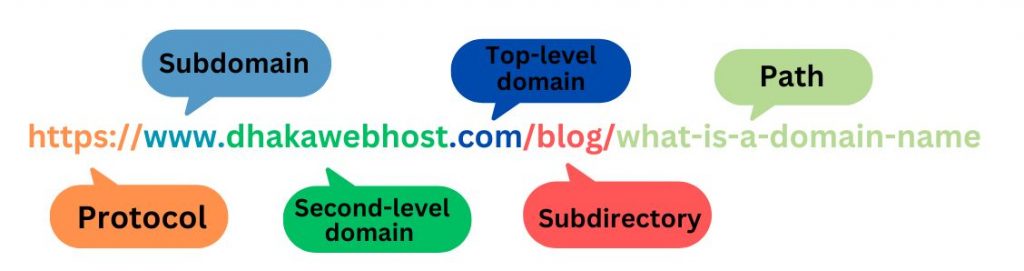
Top-level domains are the topmost level for naming in the DNS hierarchical structure. TLDs come after the dot in your domain: for example, “.com” in “dhakawebhost.com.”. TLDs are regulated by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) and are divided into several groups:
Generic Top-Level Domains (gTLDs)
GTLDs are the most common form of TLD and are for general use; hence, all persons can normally register them without restriction. Popular GTLDs include:
- .com: Most utilized and known amongst commercial entities.
- .net: Mostly applied by websites based upon networking and technology.
- .org: Used for non-profit organization purposes.
- .info: Associated with informational sites.
Country Code Top-Level Domains (ccTLDs)
Country Code TLDs apply to a certain country or territory. They will be useful in targeting websites to a particular geographical audience. Some examples of ccTLDs include:
- .bd (Bangladesh)
- .us (United States)
- .uk (United Kingdom)
- .ca (Canada)
- .de (Germany)
Sponsored Top-Level Domains (sTLDs)
The sponsored TLDs are those currently operated by private organizations that represent a particular community or purpose. The requirements for registration are more restricted, and such TLDs can be utilized in contexts where the website falls within the objectives of the sponsor. Examples of sTLDs include:
- .edu: For educational institutions only.
- .gov: For government-related bodies only.
- .mil: For military organizations.
Second-Level Domains (SLDs)
Second-level domains are the part of the domain name before the top-level domain, usually the brand or business name. For example, in example.com, example is the second-level domain. The SLD can affect your branding and SEO, as it is often a keyword that will be typed by users to locate your business. A memorable and unique SLD leads to good brand recall and enhances user experience.
Subdomains
In other words, it’s the addition of a prefix to an already existing domain. In some words, you are creating a child under a parent domain. Subdomains can also be useful to help different sections of your website or special regions or audiences. Examples include:
- blog.example.com: This could be used by individuals hosting blogs on their sites.
- shop.example.com: This is mostly used when someone wants to host an online store.
Subdomains help in organizing a large website for focused content with coherence to the brand.
Internationalized Domain Names (IDNs)
Internationalized Domain Names can be registered in non-Latin scripts, for example, Arabic, Chinese, or Cyrillic. Such domain names target international groups and facilitate the searching and recognition of websites by non-English speakers with similar spelling and writing.
New Generic Top-Level Domains (new gTLDs)
New gTLDs have opened a whole world of domain name possibilities in recent years, allowing businesses and individuals to select extensions that are representative of their industry, purpose, or interests. Some of these new gTLDs may include the following:
- .tech: Best suited for technology-based websites.
- .store: Mainly used by e-commerce companies.
- .blog: wanted by bloggers.
- .photography: desired for photography-based websites.
New gTLDs allow for great opportunities in unique branding and, therefore, a memorable web address targeting a specific niche.
Exact Match Domains (EMDs)
Exact Match Domains are domain names that include the popular keyword or search query in them, such as “bestshoes.com” or “buybooks.com.” EMDs were highly valuable for SEO at one time, as they perfectly coincided with search queries, thus offering potential advantages regarding ranking positions in search engines. But modern search engines give relevance to qualitative content over an EMD, though EMDs still can have their value in branding and user trust.
Third-Level Domains
Third-level domains go one step beyond, often used by large organizations to distinguish their various departments or regions. They essentially extend the hierarchy and can be used in respect to specific divisions, such as:
- us.walmart.com: U.S. Walmart.
- de.company.com: For Germany-the German branch of a company.
Third-level domains are useful for enterprises working internationally or across more than one department, thus allowing a much more organized web presence.
How to Choose the Right Type of Domain for Your Website
The type of domain to use largely depends on the purpose of your website, the target audience, and your brand identity. Here are some tips to guide your decision:
Global Reach: Optimize for internationally recognized gTLDs, such as .com, or new gTLDs that reflect your industry, for example, .tech for technology companies.
Local Presence: If you serve a country, a ccTLD (.uk, .ca) could work out in reaching those users.
Non-Profits or Education: Consider sTLDs like .org and .edu to gain immediate trust and credibility.
For Unique Branding: Search for branded or premium domains, and go for a new gTLD if it really adds value to your brand identity.
Why Dhaka Web Host as the domain provider?
Competitive Price with No Hidden Charges
DWH offers the best price class for domain name registrations and renewals; hence, it allows for proper budgeting without hidden charges.
Free DNS Management and Easy Transfers
Our free DNS management facilities will ease the headache of managing your domain settings, and our support team will facilitate domain transfers without any hassle.
Quick and Simple Registration
Register your domain name in minutes—a fast and friendly registration process awaits you at DWH with many different extensions.
Easy Payment Plans
Among all the different means of payment, two of those in use by locals include bKash.
Full Domain Control Panel
The Control Panel for DWH is a convenient, easy-to-use way to be in control of the settings of your domain.
Final Thoughts
Knowledge of different types of domains and their uses can make a wide difference in branding your website, user experience, and even visibility in search engines. Each type of domain has its own unique benefits and use cases; hence, consider the audience, the goal, and the industry before choosing one. You can select the right domain to establish a strong presence and trust with your audience from the moment they see your URL.

