The foundation of your online presence is your domain name. It’s one of the most crucial things for your visitors to understand and keep in mind, and it’s also a vital part of your digital marketing plan. As a result, understanding what a domain is can help you set up your online presence for success, especially if you own a business and want to boost sales through your website.
We’ve written this comprehensive guide to help you learn about domain names and how to register your own domain name to run your own website.
What is a domain name?

The address, visitors type into their browser to access a website is called a domain name. Each domain name is specific to a certain website, similar to a fingerprint. In order to make it easier for people to access the Internet Protocol (IP), which serves as a website’s online identifier, domains were developed.
Dhakawebhost’s domain name is dhakawebhost.com. Users can find the main Dhaka Web Host website using that domain name.
Why Do You Need a Domain Name?
Any business, organization, or individual striving to establish an online presence should own a domain name. A combination of a domain name, website, and email address forms your unique identity online. That, in turn, helps your business create a professional look, increase brand awareness, build credibility, and protect your trademarks and copyrights.
How Do Domains Work?

Every website has two main elements – a domain name and a web hosting server. All domain names are linked to their respective IP addresses and point to the specific web servers that host the websites.
The DNS servers get a request when you type a domain name into a web browser. DNS servers look for the servers associated with that particular domain name and route your request to those servers. The “name servers” are controlled by the web hosting company. They will send the request to the web server that hosts the specific website’s files after locating the relevant IP. The IP is used by the web server to locate all connected files and transmit them all back to the browser. These processes are completed in less than 3 seconds. A domain server is another name for a DNS or web server.
Difference between a domain and a subdomain?
The web address you purchase from a domain registry is a domain, such as dhakawebhost.com. A subdomain is part of a domain that can be made by the owner of the domain (for example, blog.dhakawebhost.com).
Difference between a domain and a URL?
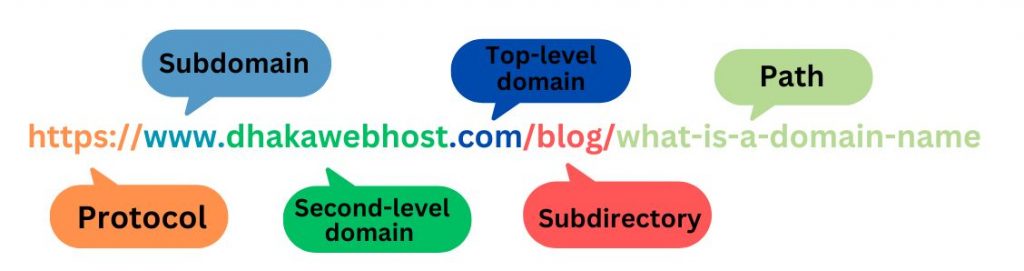
The URL contains the domain name. This is where the site’s primary website address is located. The Universal Resource Locator (URL) connects to a particular page of a website and provides several other pieces of information about the site, however, every URL includes the domain name.
The address displayed while a user navigates a website may be longer than just the domain name that they typed in for the address bar.
For example, DhakaWebHost’s domain is:
dhakawebhost.com
However, the URL for this page is:
https://dhakawebhost.com/blog/what-is-a-domain
In the URL, https:// is the transfer protocol. In this case, it is https rather than just http. This indicates that the webpage has an SSL certificate, which secures the information the page sends and receives by encrypting it.
Then comes dhakawebhost.com, which is the actual domain name. This consists of a second-level domain, dhakawebhost, which is the specific name that comes first, and the top-level domain, which is .com.
Finally, you see /blog and /what-is-a-domain, which are the path and the slug for the specific page on that domain that the user is visiting.
The Parts of a Domain Name
A domain normally consists of two components: the top-level domain and the second-level domain. These parts get less specific as you read from left to right.
Second-Level Domain (SLD): The second-level domain serves as your website’s special identification. It is the portion of your domain name that appears before “.com” or another extension.
If you’re creating a website for your company, think about purchasing a domain that contains the name of your company. This can help people locate your website more quickly without them having to spend a lot of time searching Google for it. As an example, “dhakawebhost” is the second-level domain of dhakawebhost.com.
Top-Level Domain (TLD): The extension of your domain, or the section that comes after your second-level domain, is known as the top-level domain.
It details the legal entity type that your company registers as on the internet. For instance, dhakawebhost’s top-level domain is “.com”.
Domain Name Types
The suffix, or the last part of a domain name, is known as a top-level domain (TLD). A small number of predefined suffixes are available, like:
- .com – commercial business (the most common TLD)
- .org – organizations (typically, nonprofit)
- .gov – government agencies
- .edu – educational institutions
- .net – network organizations
- .mil – military
Generic top-level domains (gTLDs) and country-code top-level domains (ccTLDs) are the two primary categories into which TLDs are classified.
The term “generic top-level domain” (gTLD) refers to a top-level domain name that indicates the domain class it belongs to (e.g.,.com,.org, or.edu).
A two-letter domain extension, such as .uk or .fr, known as a country code top-level domain (ccTLD) is given to a nation, region, or territory.
Because they are more specific, adaptable, and suitable, nTLDs are new top-level domain names that are targeted toward businesses, organizations, and services. The nTLDs “.voyage”, “.app”, “.ninja”, “.cool”, etc. are some examples.
How do I Choose a Domain Name?
Pick a name that is simple to type and say. If consumers have trouble pronouncing or spelling it correctly, it will harm your brand and make the name less memorable.
Choose a domain that can be developed into a brand. Exact and partial keyword match domain names are bad since they are very generic and challenging to brand. Additionally, you should avoid using numbers and hyphens in your domain name because they are difficult to remember and pronounce.
Short and simple is best. Long, complicated domain names carry a significant chance of typos and misspellings. That’s just something we don’t need.

Avoid using names that can be mistaken for current brands. You are terribly wrong if you believe you can capitalize on the success of another brand. When you are sued, brand confusion will be the least of your concerns.
Make use of the proper extension. You’d think that everyone would go with a TLD with a catchy extension like .blackfriday,” given how the new TLDs are taking the internet by storm. To remain with the tried-and-true “.com” is the recommendation that most marketers provide, simply because it is the suffix that is most familiar outside of the tech community. ccTLDs are definitely a better option for your company if you’re targeting a local market.
Pick a name for your company that clearly describes what it does. Be careful not to take things too literally. But any business can greatly benefit from a clever domain name that tells visitors what to expect when they visit your website.
What Is a Domain Registrar, and Who Manages Domain Names?
You might be wondering where exactly domain names originate. Who makes the decisions regarding which top-level domains are appropriate for use as the addresses of websites?
The Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers, also known as ICANN, manages TLDs.

It is a non-profit organization that creates and brings into effect domain name regulations, chooses the available domain endings, and is also in charge of the technical care of the infrastructure in the background.
However, they are not the people you will deal with when you attempt to purchase a domain name. Instead, you will consult a domain registrar or domain seller under the registrar for that.
Companies that sell domain names to customers are known as domain registrars because of their agreements with ICANN. As well as registering the domains, managing records and renewals, offering customer service, and moving them to other registrars, they are also in charge of all of these tasks.
Domain registrars, in a nutshell, are the business-oriented, client-facing side of domain name registration and management. On the other hand, ICANN just serves as its governing body.
How to Register a Domain Name
When you register a domain name, you are essentially reserving that name for your own use. No one else can use that domain name as long as you continue to renew it. And you will have to renew it each year with a domain registrar service.
Domain names are typically registered through domain name registrars. The process is usually pretty simple and straightforward. Once you’ve registered a domain name, you’ll need to point it to your web hosting provider or your own servers. This will tell the domain name where to find your website.

How to Transfer a Domain Name
To transfer a domain from one registrar to another, please check whether you have completed these steps.
- A domain must be unlocked from your domain control panel before transferring. You can check the transfer status of a domain using WHOIS CHECKER. If the domain transfer status shows “ClientTransferProhibited”, you need to unlock the Domain transfer lock or disable theft protection from your domain control panel. If you cannot do it yourself, ask your previous registrar’s help to unlock the domain transfer.
- You need an EPP code or Authorization Key to transfer a domain from one registrar to another. You can get your EPP code or Authorization Key from your domain control panel or ask your previous registrar to provide your EPP code.
- After getting the EPP code, you need to order a domain transfer with your EPP code from our website. An email notification will be sent to your email address instantly when you make payment for the transfer. Remember, it will take up to 5-7 working days to complete the transfer. If your transfer fails for any reason, you will get an email from your previous registrar. Please check your email regularly and check WHOIS CHECKER to see your domain transfer status with the new registrar.
- If the domain is transferred to us successfully, you can manage your domain from the Dhaka Web Host domain control panel.
How to Keep Your Domain Name Secure
A domain name has significant business value. Therefore, maintaining its security must come first and foremost. You may do that with the help of the following suggestions:
- Pick a reliable registrar or seller, like dhakawebhost.com.
- Be as careful as you can with your contact information and any registration-related personal information.
- Never reveal the login details for your domain registration.
- Keep an eye out for emails asking for login information (phishing). You don’t need to share your username and password because the majority of domain registrars never openly request this information.
- Make two-factor authentication available. Having a code provided to you via phone or email gives an additional layer of protection against attacks.
Final Thoughts
A domain name is a unique address that opens a website. Many advantages come with having a custom domain name, including enhanced SEO, branding, and memorability.
We covered the functions of domain names, their various kinds, and how to register and transfer a domain name in this post.
We hope that this post has provided you with a basic understanding of domain names and how to use them for projects or internet businesses.